Other references
Definitions
These definitions have been greatly simplified for brevity and do not cover every aspect of each topic.
Aa lava: A type of basaltic lava having a rough, jagged, clinkery surface and a vesicular interior.
Available water capacity: The amount of soil water available to plants to the depth of the first root-restricting layer.
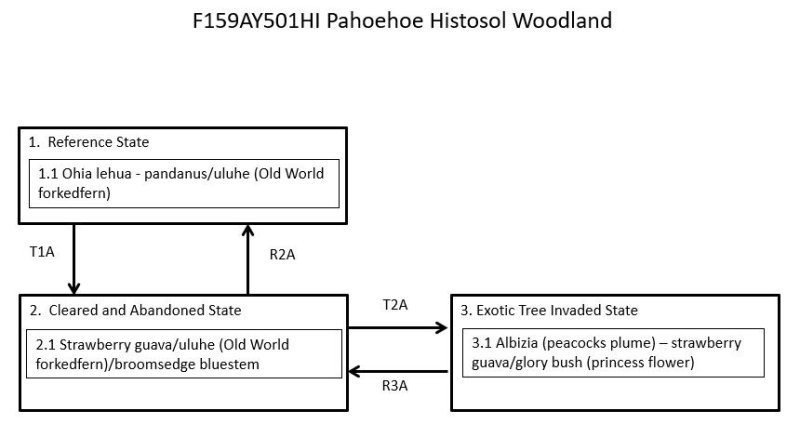
Community pathway: A description of the causes of shifts between community phases. A community pathway is reversible and is attributable to succession, natural disturbances, short-term climatic variation, and facilitating practices, such as grazing management.
Community phase: A unique assemblage of plants and associated dynamic soil properties within a state.
Dominant species: Plant species or species groups that exert considerable influence upon a community due to size, abundance, or cover.
Drainage class: The frequency, duration, and depth of a water table in a soil. There are seven drainage classes, ranging from “excessively drained” (soils with very rare or very deep water tables) to “well drained” (soils that provide ample water for plant growth but are not so wet as to inhibit root growth) to “very poorly drained” (soils with a water table at or near the surface during much of the growing season that inhibits growth of most plants).
Electrical conductivity (EC): A measure of the salinity of a soil. The standard unit is deciSiemens per meter (dS/m), which is numerically equivalent to millimhos per centimeter (mmhos/cm). An EC greater than about 4 dS/m indicates a salinity level that is unfavorable to growth of most plants.
Isohyperthermic soil temperature regime: A regime in which mean annual soil temperature is 72 degrees F (22 degrees C) or higher and mean summer and mean winter soil temperatures differ by less than 11 degrees F (6 degrees C) at a specified depth.
Isothermic soil temperature regime: A regime in which mean annual soil temperature is 59 degrees F (15 degrees C) or higher but lower than 72 degrees F (22 degrees C) and mean summer and mean winter soil temperatures differ by less than 11 degrees F (6 degrees C) at a specified depth.
Kipuka: An area of land surrounded by younger (more recent) lava. Soils and plant communities within a kipuka are older than, and often quite different from, those on the surrounding surfaces.
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA): A geographic area defined by NRCS that is characterized by a particular pattern of soils, climate, water resources, and land uses. The island of Hawaii contains nine MLRAs, some of which also occur on other islands in the state.
Naturalized plant community: A community dominated by adapted, introduced species. It is a relatively stable community resulting from secondary succession after disturbance. Most grasslands in Hawaii are in this category.
Pahoehoe lava: A type of basaltic lava with a smooth, billowy, or rope-like surface and vesicular interior.
Parent material: Unconsolidated and chemically weathered material from which a soil is developed.
Perudic soil moisture regime: A very wet regime found where precipitation exceeds evapotranspiration in all months of normal years. On the island of Hawaii, this regime is found on top of Kohala and on parts of the windward side of Mauna Kea.
pH: The numerical expression of the relative acidity or alkalinity of a soil sample. A pH of 7 is neutral; a pH below 7 is acidic and a pH above 7 is basic.
Reference community phase: The phase exhibiting the characteristics of the reference state and containing the full complement of plant species that historically occupied the site. It is the community phase used to classify an ecological site.
Reference state: A state that describes the ecological potential and natural or historical range of variability of an ecological site.
Restoration pathway: A term describing the environmental conditions and practices that are required to recover a state that has undergone a transition.
Sodium adsorption ratio (SAR): A measure of the amount of dissolved sodium relative to calcium and magnesium in the soil water. SAR values higher than 13 create soil conditions unfavorable to most plants.
Soil moisture regime: A term referring to the presence or absence either of ground water or of water held at a tension of less than 1500 kPa (the crop wilting point) in the soil or in specific horizons during periods of the year.
Soil temperature regime: A defined class based on mean annual soil temperature and on differences between summer and winter temperatures at a specified depth.
Soil reaction: Numerical expression in pH units of the relative acidity or alkalinity or a soil.
State: One or more community phases and their soil properties that interact with the abiotic and biotic environment to produce persistent functional and structural attributes associated with a characteristic range of variability.
State-and-transition model: A method used to display information about relationships between vegetation, soil, animals, hydrology, disturbances, and management actions on an ecological site.
Transition: A term describing the biotic or abiotic variables or events that contribute to loss of state resilience and result in shifts between states.
Udic soil moisture regime: A regime in which the soil is not dry in any part for as long as 90 cumulative days in normal years, and so provides ample moisture for plants. In Hawaii it is associated with forests in which hapuu (tree ferns) are usually moderately to highly abundant.
Other References
Armstrong RW. 1973. Atlas of Hawaii. University of Hawaii Press, Honolulu.
Athens JS. Ch. 12 Hawaiian Native Lowland Vegetation in Prehistory in Historical Ecology in the Pacific Islands – Prehistoric Environmental and Landscape Change. Kirch PV and TL Hunt, eds. 1997. Yale U. Press, New Haven.
Burney DA, HF James, LP Burney, SL Olson, W Kikuchi, WL Wagner, M Burney, D McCloskey, D Kikuchi, FV Grady, R Gage II, and R Nishek. 2001. Fossil evidence for a diverse biota from Kauai and tis transformation since human arrival. Ecological Monographs 71:615-641.
Craighill ES and EG Handy. 1991. Native Planters in Old Hawaii – Their Life, Lore, and Environment. Bernice P. Bishop Museum Bulletin 233, Bishop Museum Press, Honolulu, HI
Cuddihy LW and CP Stone. 1990. Alteration of Native Hawaiian Vegetation: Effects of Humans, Their Activities and Introductions. Honolulu: University of Hawaii Cooperative National Park Resources Study Unit.
Giambelluca TW and TA Schroeder. 1998. Climate. In: Atlas of Hawaii, 3rd edition. SP Juvik, JO Juvik, and RR Paradise, eds. pp. 49-59. Honolulu: University of Hawaii Press.
Hazlett RW and DW Hyndman. 1996. Roadside Geology of Hawaii. Mountain Press Publishing Company, Missoula MT.
Henke LA. 1929. A Survey of Livestock in Hawaii. Research Publication No. 5. University of Hawaii, Honolulu.
Jacobi JD. 1989. Vegetation Maps of the Upland Plant Communities on the Islands of Hawaii, Maui, Molokai, and Lanai. Technical Report 68. Cooperative National Park Resources Studies Unit, University of Hawaii at Manoa and National Park Service.
Juvik JO and D Nullet. 1993. Relationships between rainfall, cloud-water interception, and canopy throughfall in a Hawaiian montane forest. In: Tropical Montane Cloud Forests. Proc. Int. Sym., San Juan, PR. Hamilton LS, JO Juvik, and FN Scatena, eds. East-West Center.
Kirch PV. 1982. The impact of the prehistoric Polynesians in the Hawaiian ecosystem. Pacific Science 36(1):1-14.
Kirch PV. 1985. Feathered Gods and Fishhooks: An Introduction to Hawaiian Archaeology and Prehistory. Honolulu: University of Hawaii Press.
Kirch PV. 2000. On the Road of the Winds: An Archaeological History of the Pacific Islands Before European Contact. Berkeley: University of California Press.
Leopold LB. 1949. The interaction of trade wind and sea breeze, Hawaii. Journal of Meteorology 6: 312-320.
Little EL Jr. and RG Skolmen. 1989. Common Forest Trees of Hawaii (Native and Introduced). US Department of Agriculture-US Forest Service Agriculture Handbook No. 679. (out of print). Available at www.fs.fed.us/psw/publications/documents/misc/ah679.pdf
Maly K and O Maly. 2004. He Moolelo Aina: A Cultural Study of the Puu O Umi Natural Area Reserve and Kohala-Hamakua Mountain Lands, Districts of Kohala and Hamakua, Island of Hawaii. Kumu Pono Associates, Hilo HI.
Mueller-Dombois D and FR Fosberg. 1998. Vegetation of the Tropical Pacific Islands. Springer-Verlag New York, Inc.
Palmer DD. 2003. Hawaii’s Ferns and Fern Allies. University of Hawaii Press, Honolulu.
Pratt HD. 1998. A Pocket Guide to Hawaii’s Trees and Shrubs. Mutual Publishing, Honolulu.
Ripperton JC and EY Hosaka. 1942. Vegetation zones of Hawaii. Hawaii Agricultural Experiment Station Bulletin 89:1-60.
Rock JF. The Indigenous Trees of the Hawaiian Islands. 1st edition 1913, reprinted 1974, Charles E. Tuttle Company, Rutland, VT and Tokyo, Japan.
Schroeder TA. 1981. Characteristics of local winds in northwest Hawaii. Journal of Applied Meteorology 20: 874-881.
Shoji SD, M Nanzyo, and R Dahlgren. 1993. Volcanic Ash Soils: Genesis, Properties and Utilization. Elsevier, New York.
Sohmer SH and R Gustafson. 2000. Plants and Flowers of Hawaii. University of Hawaii Press, Honolulu.
Soil Survey Staff. 1999. Soil Taxonomy – A Basic System of Soil Classification for Making and Interpreting Soil Surveys. USDA – NRCS Agriculture Handbook Number 436.
Steadman DW. 1995. Prehistoric extinctions of Pacific island birds: biodiversity meets zooarchaeology. Science 267:1123-1131.
USDA-NRCS-PIA T&E Species GIS files. Not publicly available.
USDA-SCS. 1972. Soil Survey of Islands of Kauai, Oahu, Maui, Molokai, and Lanai, State of Hawaii. Foote DE, Hill EL, Nakamura S, and F Stephens, in cooperation with The University of Hawaii Agricultural Experiment Station.
USDI-USGS. 2006. A GAP Analysis of Hawaii. Final Report and Data.
Vitousek P. 2004. Nutrient Cycling and Limitation: Hawaii as a Model Ecosystem. Princeton University Press, Princeton and Oxford.
Wagner WL, DR Herbst, and SH Sohmer. 1999. Manual of the Flowering Plants of Hawaii, Revised Edition. Bishop Museum Press, Honolulu.
Whistler WA. 1995. Wayside Plants of the Islands: A Guide to the Lowland Flora of the Pacific Islands. Isle Botanica, Honolulu.
Contributors
David Clausnitzer
John Proctor
Amy Koch
Mike Kolman
Mathew Cocking
Carolyn Wong
Kendra Moseley
Jennifer Higashino
Approval
Kendra Moseley, 4/17/2025
Acknowledgments
Assistance, advice, review, and/or insights:
Randy Bartlett, Puu Kukui Watershed Preserve
Alison Cohan, The Nature Conservancy
Michael Constantinides, NRCS-PIA
Gordon Cran, Kapapala Ranch
Diana Crow, Ulupalakua Ranch
Lance DeSilva, Hawaii DLNR
Kerri Fay, Waikamoi Preserve, The Nature Conservancy
Alex Franco, Kaupo Ranch
Ranae Ganske-Cerizo, NRCS
Carl Hashimoto, NRCS
Jennifer Higashino, USFWS and NRCS
Bob Hobdy, consultant, Maui
Wallace Jennings, NRCS
Mel Johansen, The Nature Conservancy
Jordan Jokiel, Haleakala Ranch
Mike Kolman, NRCS
David Leonard, volunteer
Penny Levin
Reese Libby, GIS - NRCS
Hannah Lutgen, Maui SWCD
Joseph May, NRCS
Scott Meidel, Haleakala Ranch
Anna Palomino, Hoolawa Farms Inc.
Jon Price, USGS
Tamara Sherrill, USFWS, Maui Nui Botanical Garden
Amber Starr, Hana Ranch
Kahana Stone, NRCS
Mark Vaught, Water Resources, Alexander & Baldwin
Jacqueline Vega, NRCS
Rich von Wellsheim, Whispering Bamboos, Kipahulu
Carolyn Wong, NRCS