Natural Resources
Conservation Service
Ecological site R028AY234UT
Semidesert Shallow Loam (Utah juniper-Salina wildrye)
Last updated: 5/02/2025
Accessed: 10/19/2025
General information
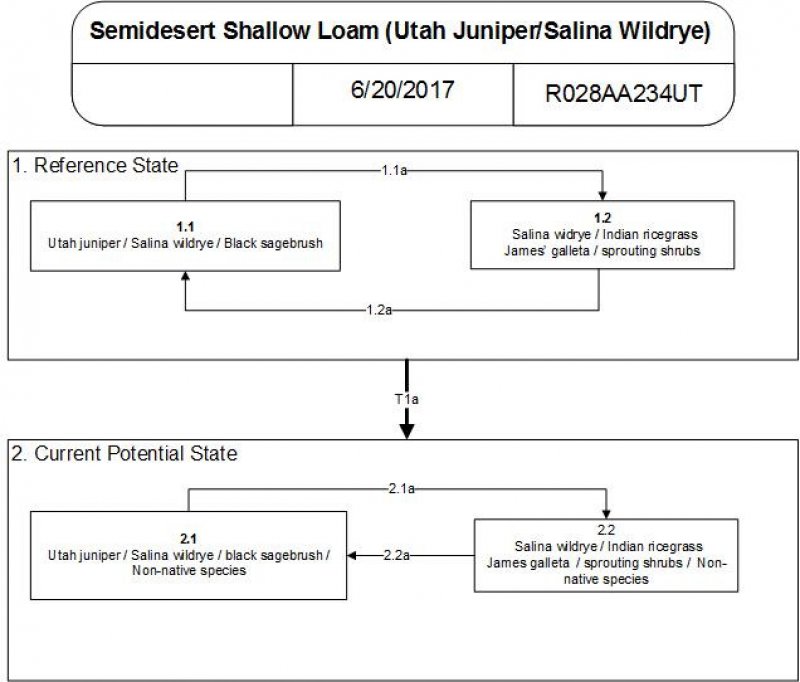
Provisional. A provisional ecological site description has undergone quality control and quality assurance review. It contains a working state and transition model and enough information to identify the ecological site.
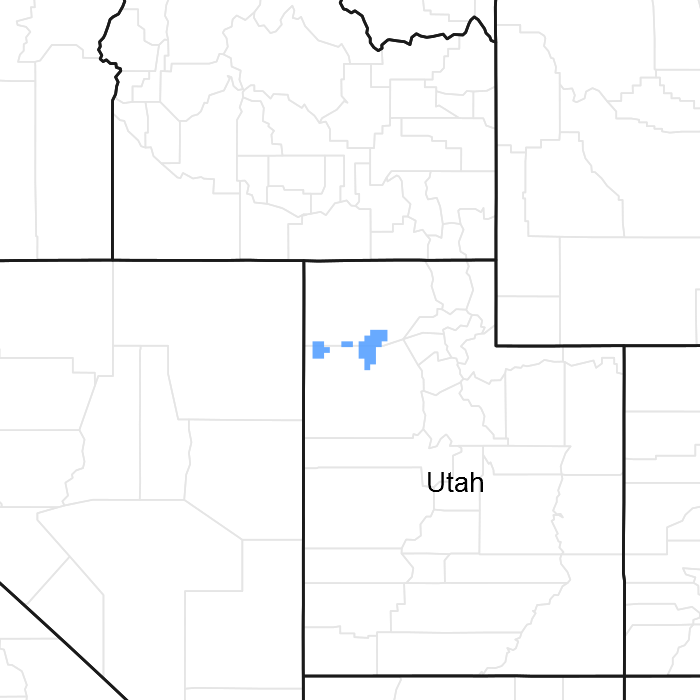
Figure 1. Mapped extent
Areas shown in blue indicate the maximum mapped extent of this ecological site. Other ecological sites likely occur within the highlighted areas. It is also possible for this ecological site to occur outside of highlighted areas if detailed soil survey has not been completed or recently updated.
MLRA notes
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA): 028A–Ancient Lake Bonneville
MLRA 28A occurs in Utah (82 percent), Nevada (16 percent), and Idaho (2 percent). It encompasses approximately 36,775 square miles (95,246 square kilometers). A large area west and southwest of Great Salt Lake is a salty playa. This area is the farthest eastern extent of the Great Basin Section of the Basin and Range Province of the Intermontane Plateaus. It is an area of nearly level basins between widely separated mountain ranges trending north to south. The basins are bordered by long, gently sloping alluvial fans. The mountains are uplifted fault blocks with steep side slopes. Most of the valleys are closed basins containing sinks or playa lakes. Elevation ranges from 3,950 to 6,560 feet (1,204 to 2000 meters) in the basins and from 6,560 to 11,150 feet (1996 to 3398 meters) in the mountains. Much of the MLRA has alluvial valley fill and playa lakebed deposits at the surface from pluvial Lake Bonneville, which dominated this MLRA 13,000 years ago. A level line of remnant lake terraces on some mountain slopes indicates the former extent of this glacial lake. The Great Salt Lake is what remains of the pluvial lake.
Mountains in the interior of this MLRA consist of tilted blocks of marine sediments from Cambrian to Mississippian age with scattered outcrops of Tertiary continental sediments and volcanic rocks. The average annual precipitation is 5 to 12 inches (13 to 30 cm) in the valleys and ranges up to 49 inches (124 cm) in the mountains. Most of the rainfall in the southern LRU occurs as high-intensity, convective thunderstorms during the growing season (April through September). The driest period is from midsummer to early autumn in the northern LRU. Precipitation in winter typically occurs as snow. The average annual temperature is 39 to 53 °F (4 to 12 °C). The freeze-free period averages 165 days and ranges from 110 to 215 days, decreasing in length with increasing elevation. The dominant soil orders in this MLRA are Aridisols, Entisols, and Mollisols. Soils are dominantly in the mesic or frigid soil temperature regime, aridic or xeric soil moisture regime, and mixed mineralogy. The soils are generally well drained, loamy or loamy-skeletal, and very deep.
LRU notes
The Basin and Range North LRU exhibits dry summer with stronger xeric patterns than the Basin and Range South LRU. Ranges in the north LRU are about 50 percent Paleozoic sedimentary/metasedimentary (limestone/quartzite dominant) and about 10 percent Tertiary volcanics. The basin floors are between 4,200 and 5,100 feet (1280 to 1554 meters) in elevation. Pinyon and juniper sites have a greater percentage of Utah juniper (Juniperus osteosperma) in the plant community than pinyon pine (Pinus edulis or monophylla). The Basin and Range North have few semidesert ecological sites with Utah juniper. Cool season grasses, such as bluebunch wheatgrass (Pseudorogneria spicata), are dominant in the plant community, while warm season grasses are largely absent or a small component of the plant community.
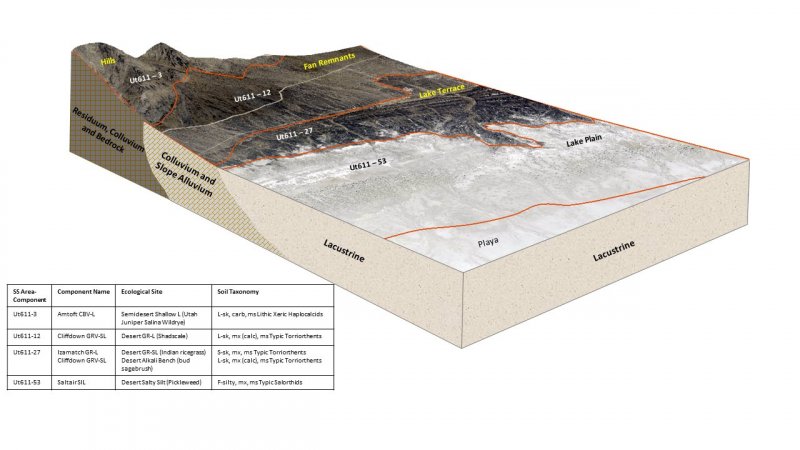
Ecological site concept
The Semidesert Shallow Loam (Utah juniper-Salina wildrye) site is unique from other shallow Utah juniper sites in that it is dominated by Salina wildrye (Leymus salinus) in the understory instead of blueblunch wheatgrass, which is the typical dominant grass. The Utah juniper canopy is typically open and black sagebrush (Artemisia nova) and Salina wildrye dominant the understory. The Semidesert Shallow Loam (Utah juniper-Salina wildrye) site occurs on mountainsides and hillsides and on soils less than 20 inches deep. It is also typically found on steep slopes (30 to 70 percent). This site is very similar to R028AY237UT and it appears that the two sites were developed concurrently with two separate soil surveys, UT611 and UT601, each site only occurring in one of the surveys. The Semidesert Shallow Loam (Utah juniper-Salina wildrye) site needs to be evaluated in the field along with 237UT to adequately describe the differences between these sites or to determine if they should be combined.
Associated sites
| R028AY215UT |
Semidesert Gravelly Loam (Wyoming Big Sagebrush) North This site occurs in deeper soils on more gradual slopes. |
|---|---|
| R028AY237UT |
Semidesert Shallow Loam (Salina Wildrye) There is no overstory of Utah juniper, otherwise sites are very similar and found next to each other in different surveys. |
Similar sites
| R028AY238UT |
Semidesert Shallow Loam (Utah Juniper-Bluebunch Wheatgrass) North Understory is dominated by bluebunch wheatgrass and not saline wildrye. |
|---|---|
| R028AY237UT |
Semidesert Shallow Loam (Salina Wildrye) No overstory of Utah juniper, otherwise sites are very similar. |
Table 1. Dominant plant species
| Tree |
(1) Juniperus osteosperma |
|---|---|
| Shrub |
Not specified |
| Herbaceous |
Not specified |
Click on box and path labels to scroll to the respective text.